-40%
Sammich SID with 2 x SwinSID installed / MOS 6581 8580 / SID Station synthesizer
$ 150.47
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Sammich SID music Synthesizer with SwinSID chipsSammich SID / SwinSID inside - YouTube
Video will open in a new window
[isdntekvideo]
This is a sound patch demo with SwinSID chips inside
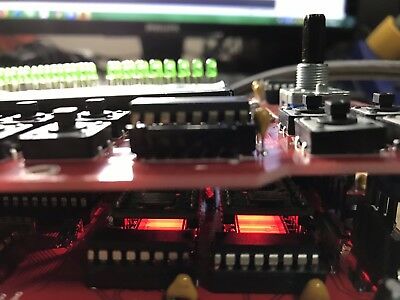
Up for sale is a newly build Sammich SID music sythesizer with 2 SwinSID chips installed.
The chips has a jumper to select between MOS 6581 or Mos 8580. You can replace the SwinSID with your own MOS chips.
I don't use arcrylic case anymore. They are soft and fragile, lots of scraches/marks overtime. That's why I am using a new design aluminum case. I've also added a fan next to the regulators. As you know the regulators generate lots of heat and the SID chip is right next to it and they are working at a very high temperature. The heat will damage the SID overtime and causing a broken filter, so a fan next to it will help releasing the heat from the regulator. The rack mount ears is optional. CNC pre-cut all sockets at the bottom of the case, you can remove them easily and plug all midi and audio sockets to the back. Add the rack mount ears and turn the unit to a rack mount unit. Optional rack mount ears will be extra including all midi & ausio sockets for installation. I only have 10 sets of rack mount ears at the moment and they only comes in black.
I am also selling Sammich FM un-assemble DIY kit
with
Yamaha YMF262 OPL3 sound chip
, check out my other listing if you are interested.
The MOS Technology 6581/8580 SID (Sound Interface Device) is the built-in Programmable Sound Generator chip of Commodore'sCBM-II, Commodore 64, Commodore 128 and Commodore MAX Machinehome computers. It was one of the first sound chips of its kind to be included in a home computer prior to the digital sound revolution. Together with the VIC-II graphics chip, the SID was instrumental in making the C64 the best-selling computer in history, and ispartly credited for initiating thedemoscene.The SID is a mixed-signal integrated circuit, featuring both digital and analog circuitry. All control ports are digital, while the output ports are analog. The SID features three-voice synthesis, where each voice may use one of at least five different waveforms: pulse wave (with variable duty cycle),triangle wave, sawtooth wave, pseudorandom noise (called white noise in documentation), and certain complex/combined waveforms when multiple waveforms are selected simultaneously. A voice playing Triangle waveform may be ring-modulated with one of the other voices, where the triangle waveform's bits are inverted when the modulating voice's msb is set, producing a discontinuity and change of direction with the Triangle's ramp. Oscillators may also be hard-synced to each other, where the synced oscillator is reset whenever the syncing oscillator's msb raises.Each voice may be routed into a common, digitally controlled analog12 dB/octave multimode filter, which is constructed with aid of external capacitors to the chip. The filter has lowpass, bandpass and highpass outputs, which can be individually selected for final output amplification via master volume register. Using a combined state of lowpass and highpass results in a notch (or inverted bandpass) output.[7] The programmer may vary the filter's cut-off frequency and resonance. An external audio-in port enables external audio to be passed through the filter.The ring modulation, filter, and programming techniques such as arpeggio (rapid cycling between 2 or more frequencies to make chord-like sounds) together produce the characteristic feel of SID music.Features:three separately programmable independent audio oscillators (8 octave range, approximately 16 - 4000 Hz)four different waveforms per audio oscillator (sawtooth, triangle, pulse, noise)one multi mode filter featuring low-pass, high-pass and band-pass outputs with 6 dB/oct (bandpass) or 12dB/octave (lowpass/highpass) rolloff. The different filter modes are sometimes combined to produce additional timbres, for instance a notch-reject filter.three attack/decay/sustain/release (ADSR) volume controls, one for each audio oscillator.three ring modulators.oscillator sync for each audio oscillator.two 8-bit A/D converters (typically used for game control paddles, but later also used for a mouse)external audio input (for sound mixing with external signal sources)random number/modulation generator